Introduction
Developing a successful digital product takes more than great ideas or advanced technology. It starts with understanding your users — what they need, what frustrates them, and what keeps them coming back. In this article, we share what we’ve learned as a UX/UI design agency, offering practical tips on how understanding users early on leads to better decisions throughout product development. When companies take the time to truly listen, they build digital products that not only meet expectations but genuinely stand out.
1. The Role of User Research in Product Development
User research is the backbone of any successful digital product. It involves collecting and analyzing data about your users to gain a deep understanding of their behaviors, challenges, and expectations. This research can be conducted through various methods such as surveys, interviews, focus groups, and direct observation. The insights gained from user research are invaluable in shaping the product strategy and ensuring that the development process is aligned with user needs.
By understanding users’ pain points and desires, product teams can prioritize features and functionalities that will have the most significant impact. For example, if user research reveals that a particular demographic struggles with navigation on similar products, the development team can focus on creating a more intuitive and user-friendly interface. Additionally, user research helps in identifying market opportunities by uncovering unmet needs or gaps in the current offerings. This allows companies to innovate and differentiate their products in the marketplace.
Moreover, incorporating user insights early in the product development process helps avoid costly redesigns and ensures that the final product is both functional and user-centric. When user needs guide the development strategy, the resulting product is more likely to achieve higher user satisfaction, engagement, and retention rates.

2. Creating User Personas and Journey Mapping
User personas and journey mapping are essential tools for translating user insights into actionable design strategies. User personas are detailed profiles that represent different segments of your target audience, based on data collected during the research phase. These personas include information such as demographic details, behavior patterns, goals, and pain points, offering a comprehensive view of the diverse needs within your user base.
Developing user personas allows teams to design with specific user groups in mind, ensuring that the product addresses the unique needs of each segment. For example, a persona might represent a young professional who values efficiency and time-saving features, while another might represent a retiree who prioritizes simplicity and accessibility. By tailoring the product to these personas, companies can create a more personalized and relevant user experience.
Share your project idea with us! If our partnership isn't the right fit, we're happy to provide valuable insights that could still benefit you.
Journey mapping complements personas by visualizing the steps users take when interacting with the product. This process involves mapping out the user journey, from the initial interaction to the final goal, highlighting key touchpoints, emotions, and potential pain points. Understanding the user journey allows teams to identify opportunities for improvement and optimization, ensuring that the product delivers a seamless and satisfying experience.
For instance, if a journey map reveals that users frequently drop off at a particular stage, it may indicate a need for redesign or additional support at that point. By using personas and journey maps, product teams can make informed design decisions that enhance usability and overall user satisfaction.

3. Prototyping and User Testing
Prototyping is a critical step in the digital product development process, allowing teams to visualize and test their ideas before moving into full-scale development. A prototype is an early model of the product that can range from basic wireframes to interactive versions that closely resemble the final product. The primary purpose of prototyping is to validate design concepts, identify potential issues, and refine the user experience based on feedback.
User testing is an integral part of the prototyping process. By involving real users in testing the prototype, teams can gather direct feedback on the product’s usability and effectiveness. User testing sessions typically involve observing how users interact with the prototype, noting any difficulties or confusion they encounter. This feedback is crucial for identifying pain points and making necessary adjustments to improve the overall user experience.
Iterating on prototypes based on user feedback is essential for creating a product that is both user-friendly and functional. Each iteration should address the issues identified during testing, gradually improving the design and performance. This iterative approach not only enhances the product’s usability but also reduces the risk of costly changes during later stages of development.
Furthermore, user testing helps validate that the product aligns with user needs and expectations. For example, if a feature is consistently misunderstood or underutilized during testing, it may indicate the need for redesign or better user education. By refining prototypes through user feedback, teams can ensure that the final product is well-received by its intended audience.
4. Implementing a User-Centric Design Approach
A user-centric design strategy is essential for creating digital products that are intuitive, accessible, and enjoyable to use. This approach emphasizes the importance of designing with the user’s needs and preferences at the forefront, ensuring that the product not only meets functional requirements but also provides a seamless and satisfying experience.
One of the core principles of user-centric design is empathy. Designers must deeply understand the challenges and expectations of their users, which involves putting themselves in the users’ shoes throughout the design process. This empathetic approach leads to the creation of products that are truly tailored to the users’ needs, resulting in higher satisfaction and adoption rates.
Aligning product features with user expectations is another key aspect of user-centric design. This involves prioritizing features that address the most critical user needs and ensuring that the interface is intuitive and easy to navigate. For example, if user insights reveal that speed and efficiency are top priorities for your target audience, the design should focus on minimizing steps and optimizing performance.
Continuous feedback and iteration are also vital components of a user-centric design approach. As the product evolves, ongoing user feedback should be used to refine and improve the design. This iterative process ensures that the product remains aligned with user needs and expectations, leading to higher user satisfaction and engagement.
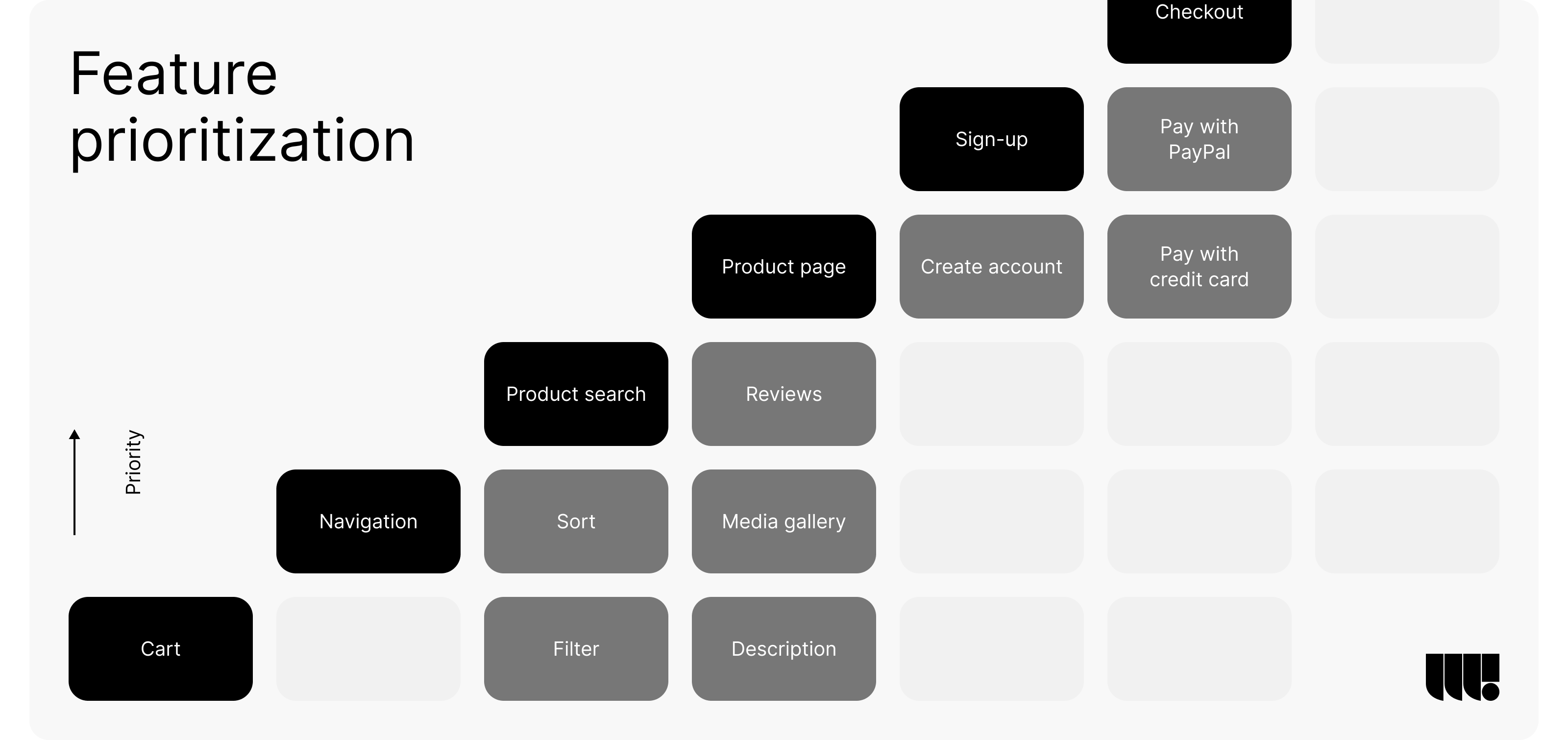
5. Analyzing User Data for Continuous Improvement
The development of a digital product doesn’t end at its launch. Continuous improvement is crucial for maintaining the product’s success in the long term, and analyzing user data plays a central role in this process. By consistently collecting and analyzing user data, teams can gain insights into how the product is being used and identify areas where enhancements can be made.
Analytics tools allow teams to track key performance metrics, such as user engagement, retention rates, and conversion rates. These metrics provide valuable insights into user behavior, helping to identify strengths and weaknesses in the product. For example, if data reveals that users are dropping off at a specific point in the user journey, it may indicate a need for design adjustments or additional support at that stage.
The feedback loop is a continuous cycle of data collection, analysis, and product optimization. By regularly reviewing user data and implementing targeted improvements, companies can ensure that their product remains relevant and competitive. This ongoing process allows the product to evolve in response to changing user needs and market conditions, leading to sustained success.
Continuous improvement also involves staying updated with industry trends and technological advancements. As user expectations evolve, it’s important to adapt the product to meet these changing demands. This proactive approach not only enhances the user experience but also drives long-term success in the digital marketplace.
Conclusion
User insights are indispensable in guiding successful digital product development. By integrating user feedback throughout the product lifecycle – from initial research to continuous improvement – companies can create products that not only meet functional requirements but also resonate deeply with users. A user-centric approach, driven by data and continuous iteration, ensures that products remain relevant, competitive, and highly valued by their target audience. Ultimately, embracing user insights is the key to developing digital products that thrive in today’s market.












